Did you know that 67.2% of businesses are prioritizing the adoption of Large Language Models and Generative AI this year? What could this mean for your organization’s future?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are deep learning algorithms that can recognize, extract, summarize, predict, and generate text based on knowledge gained during training on huge datasets. 58% of businesses have started to work with LLMs.
Over the next three years, 45.9% of enterprises aim to prioritize scaling AI and ML applications. These tools can enhance their data strategy’s business value. In the upcoming fiscal year, 56.8% anticipate a double-digit revenue increase from their AI/ML investments. Another 37% expect single-digit growth.
Are you prepared for the AI transformation in the business world? Explore the possibilities of LLMs for enterprise adoption and secure your organization’s competitive edge.
Table of Contents
What is a Large Language Model?
According to Nvidia, LLM “is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) system that is capable of generating human-like text based on the patterns and relationships it learns from vast amounts of data.” Large Language Models are trained on extensive datasets of text. These can include books, Wikipedia, websites, social media, academic papers, etc.
Such datasets range from tens of millions to hundreds of billions of data points. The size of the dataset and the volume of training data significantly impact the accuracy and sophistication of a model. LLM in enterprise also has a huge number of learnable parameters.
These enable them to excel in tasks such as content generation, summarization, and translation. Moreover, they empower LLMs to comprehend nuanced language, technical terminology, and diverse writing styles. So, Large Language Models produce responses that are more precise and refined compared to their smaller counterparts.
How Do LLMs Work?
Large Language Models function through a complex and systematic process. The key components that enable their remarkable capabilities are:
- Input Text. Raw text data serves as the foundation for these models. It represents the initial information provided for processing.
- Tokenizer. The input text undergoes tokenization, where it is broken down into smaller units such as words, phrases, or characters. Tokenization structures the text for the model’s comprehension.
- Embedding. Tokens are converted into numerical vectors through embedding. They capture the semantic and syntactic meanings of the text. Embeddings transform textual data into a format understandable by the neural network.
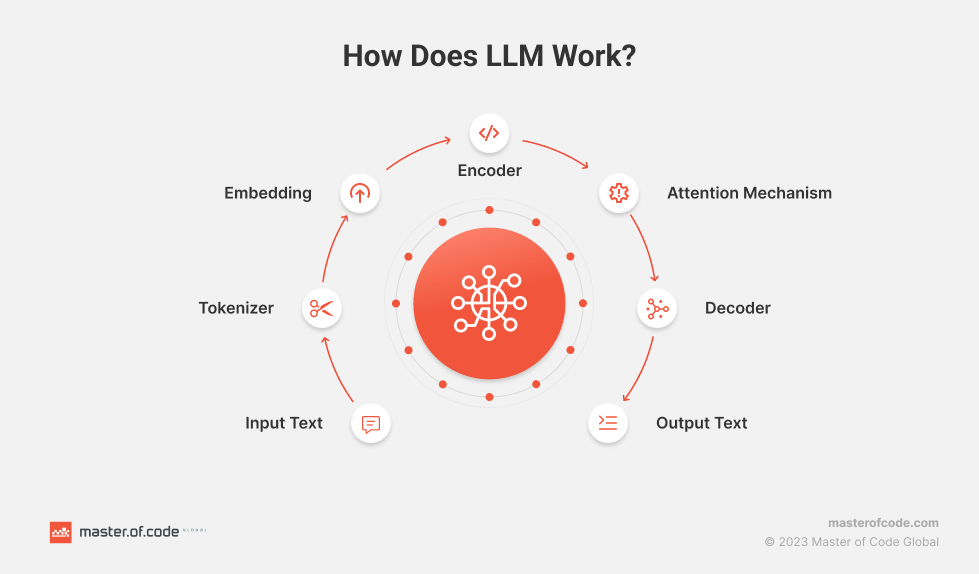
- Encoder. The encoder processes the embedded tokens. It’s a fundamental component that extracts relevant information from the input sequence. The encoder’s role is crucial in understanding the context and relationships between words.
- Attention Mechanism. This element allows the model to focus on specific parts of the input text. It assigns varying levels of importance to different tokens. Thus, it enhances the model’s ability to weigh the significance of words and improve context understanding.
- Decoder. Utilizing the encoded information, the decoder generates the output sequence. This component translates the processed data back into human-readable text. It also ensures the response is coherent and contextually relevant.
- Output Text. The final generated text is the result of the LLM’s intricate processing. It is based on the input and the model’s learned patterns and relationships.
State of LLM Adoption in Enterprises
Enterprises are increasingly recognizing the transformative power of AI. As per The State of AI in the Enterprise Report, 64% incorporate it into their business models. The drive behind this adoption is multifaceted.
32% of enterprises aim to streamline efficiency, and 20% focus on enhancing customer experiences. More than 75% of enterprises report positive outcomes from utilizing AI. Among them, 45% experienced moderate benefits, 23% substantial improvements, and 8% remarkable gains. Amidst the adoption fervor, enterprises grapple with significant challenges.
As per Enterprise Generative AI Adoption Report, top challenges hindering the adoption of Generative AI/LLMs include data-related challenges (62.9%) and the need for customization & flexibility (63.5%). In addition, organizations face concerns about security & compliance (56.4%), performance & cost (53%), and governance issues (60.2%). To address some of these challenges, 83.3% of companies plan to implement policies specific to Generative AI adoption.
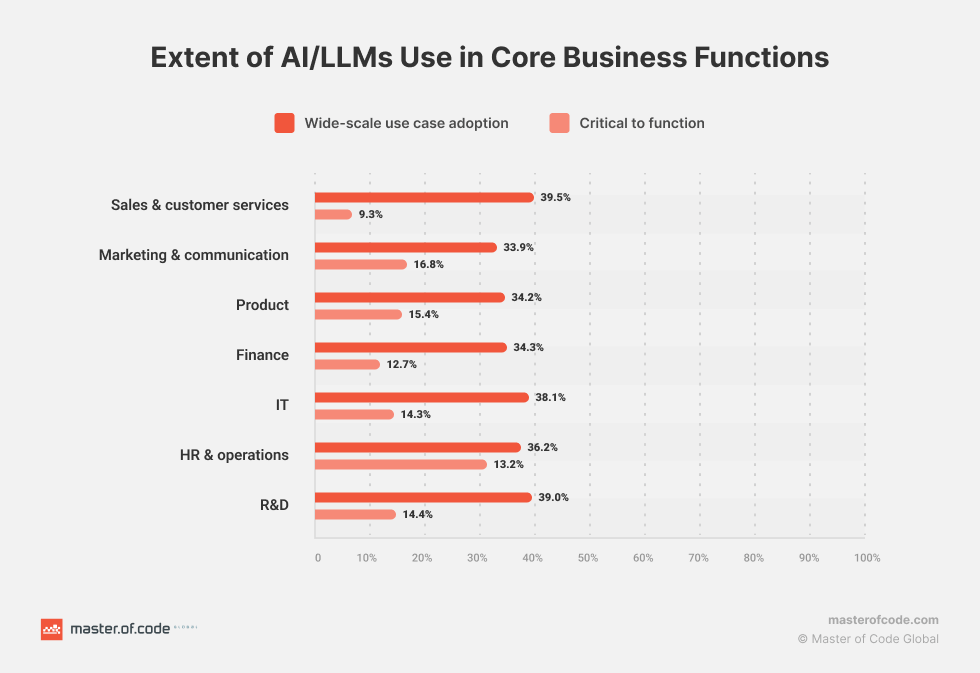
Enterprises are diversifying their use of Large Language Models beyond Generative AI. 32.6% chose information extraction, emphasizing LLMs’ insight extraction from unstructured data. Additionally, 15.2% preferred Q&A/Search, demonstrating real-time response capabilities.
As more teams look to customize the LLM for domain-specific accuracy, 32.4% opt for fine-tuning and 27% embrace reinforcement learning.
Indeed, companies are increasingly relying on customized enterprise LLMs for precise outcomes. A majority of teams intend to tailor their Large Language Models through fine-tuning (32.4%) or reinforcement learning with human feedback (27%). This highlights the need for cautious deployment of LLMs to balance innovation with ethical norms.
Benefits of Integrating Generative AI Solutions
- Improved Performance: AI Chatbots and virtual assistants can understand and respond to a wider range of language inputs. This can lead to understanding customer intent faster, higher containment rates, and improved overall customer experiences.
- Hyper-personalized Conversational Commerce: Utilizing LLMs can help enterprises create increasingly customized marketing messages and product recommendations based on individual customer profiles and preferences, leading to higher engagement, better conversion rates, and improved CSAT.
- Enhanced Search Functionality: Improving the search experience on websites, knowledge bases, and apps with the help of Generative AI solutions. NLU and LLMs allow a user to more easily describe what they are looking for, as user intent is understood faster, increasing the likelihood of delivering accurate and relevant search results.
- Multilingual Conversational Commerce: Expanding global reach and adding new market segments. Using NLU and LLMs allows for the quick training and tuning of additional languages, making it easier to offer multilingual customer support and conversational commerce solutions.
- Advanced Analytics: Leveraging NLU and LLMs to analyze large volumes of unstructured data, such as customer interactions, to identify new intents, sentiment, trends, patterns, and potential areas of improvement throughout the customer journey.
Thinking of incorporating Generative AI into your existing chatbot? Validate your idea with a Proof of Concept before launching. At Master of Code Global, we can integrate Generative AI into your current chatbot, train it, and have it ready for you in just two weeks.
LLM Enterprise Use Cases
Below is a structured look at the most common and most valuable ways organizations use enterprise Large Language Models today.
Content & Documentation Workflows
- Draft and edit emails, blog posts, reports, and creative content.
- Extract key insights from long documents or datasets.
- Summarize large volumes of information for quick review.
- Translate text into multiple languages with high fluency.
- Detect and filter inappropriate or harmful online content.
Application Development Support
- Generate code snippets tailored to specific tasks or frameworks.
- Identify bugs, errors, and potential security vulnerabilities.
- Suggest improvements to existing code for readability or performance.
- Produce documentation or clarify complex logic on request.
AI-Driven Chatbots & Conversational AI
- Answer questions and guide users through purchases or setup steps.
- Analyze customer feedback to create more personalized responses.
- Integrate Generative AI to summarize past conversations, group similar cases, and surface relevant knowledge to agents.
- Reduce escalations by giving support teams contextual information instantly.
- Improve containment and CSAT by enabling accurate self-service workflows.
Sentiment & Intent Analysis
- Detect emotional tone, sentiment, and underlying intent in text.
- Monitor shifts in brand perception across channels.
- Support marketing and PR teams with real-time insight for decision-making.
Knowledge Management
- Generative AI indexes and retrieves documents across fragmented repositories.
- Transform unstructured content into usable summaries or action points.
- Streamline internal research with concise, context-aware answers.
Predictive Analytics & Fraud Detection
- Identify trends, anomalies, or early indicators of change.
- Flag suspicious behavior or fraudulent activity based on patterns.
- Support risk management and compliance teams with clearer insights.
Sales & Marketing Activities
- Analyze customer reviews, social media mentions, and market signals.
- Anticipate buyer preferences to support targeted campaigns.
- Automate lead generation, segmentation, and outreach preparation.
- Identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities more accurately.
Read More: Check out more insights on Generative AI for Marketing
Developer Productivity & AI Copilots
- Suggest code, tests, and refactorings during development.
- Speed up onboarding by explaining repositories or modules.
- Assist with DevOps tasks such as config reviews or script generation.
- Reduce context switching by answering technical questions instantly.
Enterprise Search & Knowledge Retrieval
- Return precise answers instead of long document lists.
- Pull information from wikis, SharePoint, CRMs, and other scattered systems.
- Summarize findings into clear, actionable notes.
- Help teams avoid duplicate work by surfacing existing knowledge.
Customer Support Optimization
- Draft fast, accurate responses for agents to review.
- Classify tickets and detect user intent for quicker routing.
- Surface step-by-step solutions from internal knowledge bases.
- Reduce agent workload by handling repetitive questions automatically.
HR & Recruitment Assistance
- Screen resumes and highlight core qualifications.
- Summarize candidate profiles for faster shortlist decisions.
- Draft job descriptions, internal policies, and employee communications.
- Power HR self-service channels for payroll, benefits, and policy questions.
Large Language Models Adoption Challenges
Imagine rolling out your first LLM-powered assistant across multiple departments. IT is excited, operations see potential, and leadership expects quick wins.
But as soon as the model starts interacting with complex data and real user queries, cracks begin to show. Scaling, accuracy, and compliance all become harder than they looked on paper. When navigating the imitations of LLMs for enterprises, companies encounter multiple challenges, so let’s take a look at them.
LLM Hallucinations
Even well-tuned models can produce statements that look accurate but aren’t grounded in real data. In customer-facing systems, this can surface as an invented refund policy. In internal tools, it may appear as a misinterpreted safety guideline or a fabricated metric in a report summary.
How enterprises keep hallucinations contained:
- Limit output length: Short responses reduce the chance of drift. For example, a procurement assistant summarizing contract terms should deliver only the key legal points, not a narrative explanation.
- Use guided inputs: Instead of letting users type free-form requests, offer structured prompts that narrow the model’s choices. A sales rep generating an email can select tone presets like “empathetic” or “assertive” to anchor the model.
- Lower temperature: Reduces creativity and enforces consistency, useful when generating compliance instructions or medical intake summaries.
- Moderation layers: Block unsafe or illogical outputs before they reach an end user. A banking chatbot, for instance, should never invent interest rates or eligibility criteria.
- Feedback loops: Agents or employees can mark incorrect outputs, helping the system refine future responses.
- Domain-specific fine-tuning: When trained on verified internal documentation, the model stops speculating and stays aligned with company standards.
Data Privacy and Integration Challenges
Enterprise LLMs work best when they have context, yet the moment sensitive information enters the system, privacy and compliance become a concern. Handling LLMs at enterprise scale introduces new constraints around data lineage, retention rules, and cross-system synchronization.
Core requirements for safe integration:
- Encryption and masking: Sensitive data (names, account numbers, PHI) must remain protected through every stage of the pipeline.
- Strict access controls: Limit which systems and teams can query the model to avoid accidental exposure.
- Retention rules: Decide what the model can store, what must be deleted instantly, and what is allowed to persist.
- Scalable infrastructure: Without proper architecture, batch queries from HR or support teams can overwhelm systems and cause downtime.
Financial and Skill Constraints
The cost of building and operating safe and trustworthy LLM systems goes beyond model access. Enterprises run into expenses when adapting integrations, securing data flows, retraining the model, and monitoring it long-term.
A typical scenario: An eCommerce company launches an AI assistant for support, only to discover after two months that it needs a dedicated prompt engineer, analytics tooling, and periodic fine-tuning, none of which were in the original budget.
What organizations must prepare for:
- Usage costs: High-volume environments can generate thousands of daily API calls.
- Skill gaps: Teams without LLM knowledge struggle to evaluate outputs, understand model drift, or identify hallucinations that slip through.
- Training programs: Upskilling analysts, support agents, and product managers reduces long-term risk and dependency on external vendors.
Unintended Bias
This issue appears when LLM-based assistants tailored to specific workflows echo patterns found in its training data. Even subtle bias can affect outcomes. For example, a recruitment assistant might score certain universities higher simply because they appear more often in public datasets, not because they objectively predict performance.
How teams counter bias:
- Representative fine-tuning: Curate datasets that reflect real customer segments or diverse applicant pools.
- Bias-detection tools: Automatically flag outputs that favor one group or interpretation.
- External validation: Run critical outputs (loan explanations, hiring recommendations, legal summaries) through independent systems.
- Diverse review groups: Domain experts and social scientists often spot issues that engineers miss.
- Iterative evaluation: Bias changes as the model evolves; checks must be continuous, not one-time.
A simple illustration: A travel company tested its LLM-generated recommendations and discovered it consistently promoted destinations popular in its English-language data sources. After diversifying its training data, results finally matched global customer preferences.
Types of LLMs
The landscape of Enterprise LLMs spans open-source, closed-source, general-purpose, and domain-specific models, each suited to different operational needs. Each category sheds light on the nuanced capabilities and LLM enterprise use cases. Here are the most common types.
Open-Source LLMs
These large language models’ source code is freely available for the public to use, modify, and distribute. They are accessible to developers and researchers, encouraging collaboration and innovation.
- Examples: LLaMA 2, Alpaca, RedPajama, Falcon, and FLAN-T5.
- Benefits: free access and modifiability, community collaboration and support, foundations for diverse applications.
- Drawbacks: potential quality and performance inconsistencies, need for technical expertise for implementation and fine-tuning, and limited user support.
Closed-Source LLMs
These are proprietary models whose source code is not publicly available. They are developed and maintained by specific organizations. And access is often restricted or provided through licenses.
- Examples: Bard, GPT-4, Claude, Cohere, Gopher, LaMDA, and Jurassic.
- Benefits: rigorous quality control, consistent high-quality performance, dedicated user support, and high reliability.
- Drawbacks: licensing costs, restricted customization options, and closed ecosystem restricting flexibility.
General-Purpose LLMs
These models handle a wide spectrum of enterprise applications, from summarization to multi-language support. They are versatile and can be applied to various applications.
- Examples: GPT-3, BERT, LaMDA, Wu Dao 2.0, and Bard.
- Benefits: versatility in NLP tasks, ease of use and minimal customization, broad availability of pre-trained models.
- Drawbacks: limited task-specific optimization, resource intensiveness for complex tasks, potential lack of precision in specialized domains.
Domain-Specific LLMs
These models are trained on specialized knowledge areas such as medicine, finance, climate research, or software engineering. Because their training data is so focused, they deliver higher accuracy and more dependable reasoning in tasks that require deep subject expertise. Examples include BioBERT for biomedical content, BloombergGPT for financial analysis, StarCoder for code generation, Med-PaLM for clinical decision support, and ClimateBERT for climate-related text interpretation.
The main advantages are precision, better handling of edge cases, and lower fine-tuning requirements. The limitations are equally important: narrow applicability, reduced flexibility, and more complex adaptation for multi-domain assistants.
For chatbot and digital assistant development, Master of Code Global evaluates both specialized and general-purpose options. Our R&D work often points to balanced models such as GPT-3.5-turbo, PaLM2, or RedPajama, which offer strong conversational performance, predictable costs, and reliable behavior across a wide range of customer interactions.
Comparative Evaluation of LLMs for Task-Specific Text Generation
In this in-depth R&D study by Master of Code Global, several leading language models were assessed. The focus was on their effectiveness in tasks commonly encountered in virtual assistants and chatbots. The evaluated models are GPT-3.5-turbo, Cohere, PaLM2 – text bison, PaLM2 – chat-bison, and Fine-tuned versions of RedPajama (3B and 7B).
GPT-3.5-turbo
This is an AI model developed by OpenAI and one of the most effective versions of GPT-3. It has a high natural language text generation capability. The model can perform a variety of tasks such as text generation, answering questions, translations, code generation, and more. Developers can fine-tune this model to create custom systems. These are better suited for their specific enterprise-level needs and can be run at scale.
Cohere
This is a natural language processing platform that uses advanced deep learning models. It provides tools and APIs for analyzing text, discovering semantic relationships, and building applications based on text data. We have used Cohere Generation in our R&D. It’s suitable for interactive autocomplete, augmenting human writing processes, and other text-to-text tasks.
PaLM2 – text bison
This deep learning model specializes in text data processing. The “text-bison” version is designed to process a variety of text inputs and for maximum performance and processing quality. It can be used for classification, sentiment analysis, entity extraction, summarization, rewriting text in different styles, generating ad copy, and conceptual ideation.
PaLM2 – chat-bison
This is a variant of the PaLM2 model aimed at handling conversations and chats. The model is designed taking into account the specifics of text interactions between users. This allows it to better understand the context and generate more suitable responses. It can also support natural multi-turn conversation.
Fine-tuned RedPajama (3B and 7B versions)
RedPajama is a collaboration project between Ontocord.ai, ETH DS3Lab, Stanford CRFM, and Hazy Research to develop reproducible open-source LLMs. Two base model versions were taken for the experiment: a 3 Billion and a 7 Billion-parameter model. Overall, RedPajama is at the forefront of open-source initiatives. It enables broader access to powerful LLMs for research and customization purposes.
LLMs Evaluation R&D Results
Our study aims to assess the efficacy of several language models in addressing specific tasks. The selected types represent a mix of established platforms and emerging research initiatives. The tasks chosen for evaluation encompass various domains and complexities.
The study focused on processes such as informing customers about device upgrades, TV streaming promotions, trade-in eligibility, device compatibility, and extracting intents from customer inputs. Key evaluation criteria included adherence to instructions, avoidance of LLM hallucination, and proper output formatting.
All models, excluding RedPajama, underwent testing using a zero-shot task-specific dataset. However, RedPajama couldn’t match the selected models, so a training dataset was created. This dataset comprised 100 prompt-completion pairs for each task to fine-tune RedPajama. The evaluation test set for all models included 250 prompts, with 50 prompts assigned to each task.
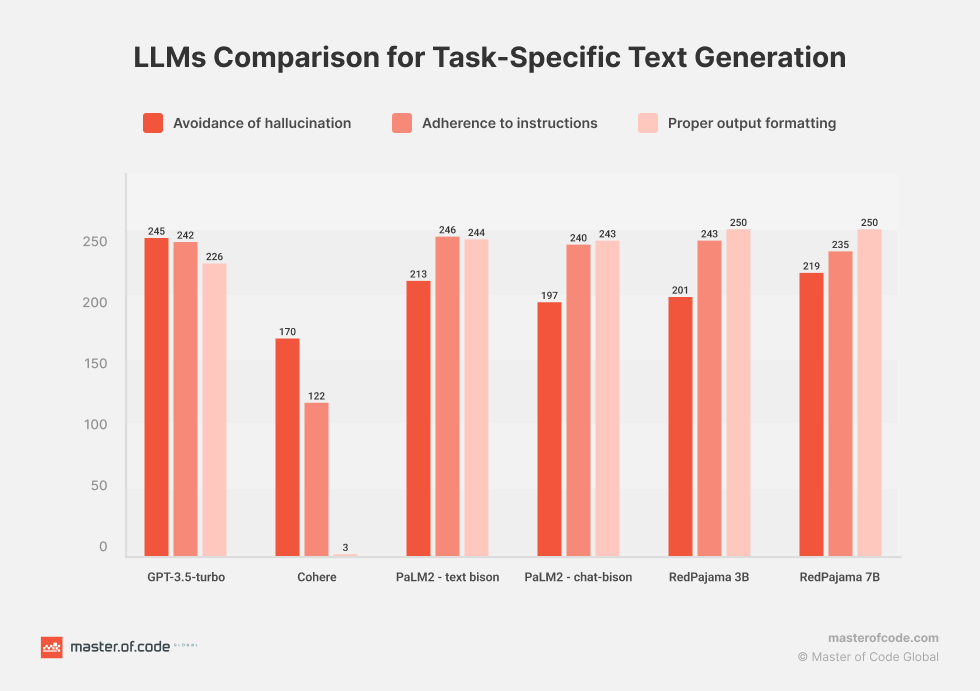
The findings revealed nuanced differences in the performance of these models. Particularly noteworthy was the consistent and robust performance exhibited by the RedPajama models. They are highly promising options for task-specific text-generation applications within the realm of virtual assistants and chatbots.
Real-Life Enterprise LLM Deployments
Adopting LLMs in enterprise environments requires more than strong models. Companies must balance performance, security, and compliance, especially when models interact with customer data or internal systems. The examples below show how global brands are using Enterprise LLM solutions in practical, controlled settings, followed by three implementations delivered by Master of Code Global.
AI Architecture Audit for Asset Management
An asset management firm approached Master of Code Global with the goal of optimizing their GenAI architecture to meet future demands. Their existing system needed a thorough assessment to identify areas for improvement, from data flow to performance and security.
We designed a comprehensive framework to evaluate their entire AI ecosystem, conducting in-depth technical reviews, stress testing, and performance benchmarking tailored to Generative AI workloads. The audit revealed an 87% potential for performance improvement, identified 8 critical security vulnerabilities, and outlined infrastructure adjustments that could triple their system’s capacity, ensuring the platform is ready for future-scale success.
Knowledge Base Automation for a Conversational AI Platform
A leading Conversational AI provider serving 18,000+ businesses needed a faster way to create and update knowledge base content. Their users were writing articles manually, which slowed the adoption of chatbot features and limited how quickly new topics could be supported.
Master of Code Global developed an LLM for enterprise application that analyzes past conversations, extracts recurring questions, and generates clear, structured articles. The system handles multiple accounts with isolated workloads and removes duplicates using embeddings and clustering. This gives teams a dependable way to maintain content without adding pressure to support operations.
Microsoft-Native AI FAQ Assistant for a Financial Institution
A regulated financial cooperative required an AI assistant to search internal policies, procedures, and compliance materials. All information had to stay inside their Microsoft environment, making external APIs unsuitable for their compliance policies.
We built an assistant powered by Power Automate’s LLM features that retrieves answers from SharePoint libraries and communicates through Teams. The solution provides fast access to information while meeting the organization’s governance expectations. This is a great example of how Enterprise LLM solutions can operate securely inside existing infrastructure.
Agentic AI Data Discrepancy Assistant for a US Energy Leader
A major energy company regularly encountered mismatches between water and oil readings, prompting slow and manual reconciliation. These discrepancies affected reporting speed and required operational staff to review data line-by-line.
We created a standalone web application with an AI agent that detects mismatches, visualizes them, and explains each issue in plain language. Built with Azure Cognitive Services and our LOFT framework, the agent turns complex data checks into easy-to-understand summaries, supporting a reliable, controlled use of scalable LLM-powered applications in industrial settings.
Airbnb: LLM-Supported Automation for High-Volume Operations
Airbnb upgraded its internal automation platform to support Enterprise LLM solutions across large-scale guest and host interactions. Their “Automation Platform v2” blends workflow rules with LLM reasoning, allowing the system to interpret incoming messages with greater contextual awareness while preserving control over core processes.
This hybrid model helps Airbnb manage high message volumes more predictably. It also provides a path for introducing scalable LLM-powered applications without disrupting existing operational structures or risk policies.
Uber: LLM-Based Invoice Interpretation
Uber introduced LLM capabilities to support financial data extraction and invoice interpretation at a global scale. The system identifies fields, checks for inconsistencies, and organizes data for downstream workflows. Its design supports enterprise audit expectations, which is essential when deploying LLMs in financial environments.
The solution reduces the manual review burden and enables faster validation cycles while keeping all activity traceable. This reflects how deploying LLMs in enterprise environments can support accuracy and control in record-heavy functions.
Microsoft: LLM Assistance Inside Finance Workflows
Microsoft’s Copilot for Finance integrates LLMs directly into Excel and Dynamics to help analysts prepare reconciliations, review variances, and generate brief explanations for data anomalies. Since it operates within the Microsoft ecosystem, the tool supports existing security and compliance requirements without adding new data pathways.
The result is a structured way for financial teams to engage with Enterprise LLM solutions during routine analysis. It also demonstrates how large organizations introduce scalable LLM-powered applications while keeping risk boundaries firmly in place.
Master of Code Global’s Approach for Enterprise LLMs
1. Turn the Business Problem Into a Precise LLM Task
We begin by reducing broad ambitions into a clear workflow the model can handle consistently. For example, replacing a 9-step support interaction with a single automated flow, or enabling employees to surface policy answers in seconds. This focus keeps scope tight and ensures the deployment targets a real efficiency gain, not a theoretical improvement.
2. Prepare Enterprise Data for Reliable Model Behavior
Enterprises often discover that their knowledge lives across CRMs, shared drives, email threads, and legacy tools. We consolidate these sources, apply permissions, and structure them so the Large Language Models for Enterprise Solutions have clean, verified inputs. This step directly reduces hallucinations and ensures the model reflects current, approved information.
3. Select and Shape the Model for the Environment
Model choice depends on precision needs, sensitivity of data, and compliance constraints. We assess whether a closed model, an open-source option, or a fine-tuned domain model is the best fit. As certified partners with AWS, Google Cloud, Salesforce, and leading LLM providers, we adapt architectures to your ecosystem rather than forcing a proprietary stack.
4. Build a Retrieval Layer That Grounds Every Response
Our LOFT serves as an enterprise framework for orchestrating retrieval, grounding, and validation across AI-driven workflows. With LOFT’s modular setup – 43% faster initial configuration and up to 20% budget savings as the project scales – the LLM receives the exact documents it needs, reducing errors and improving consistency across high-volume workflows.
5. Add Guardrails That Protect the Business
We implement safety checks, policy filters, tone controls, and action limits tailored to your environment. In regulated industries, this may mean restricting the model to summaries only; in customer-facing systems, it may involve strict fallback rules or multi-step validation. Every safeguard is designed to prevent unintended changes in CRMs, order systems, or knowledge repositories.
6. Integrate Thoughtfully Into Existing Systems
Our engineering teams specialize in custom integrations across platforms and proprietary CRMs. The model only reads or writes where allowed, and every action is logged. This avoids the common failure mode where LLMs introduce silent inconsistencies in downstream systems.
7. Measure Performance With Business-Critical Metrics
We track factual accuracy, containment, reduction in handling time, and quality scores from internal reviewers. These KPIs ensure the system delivers outcomes comparable to the results we’ve driven for global brands like T-Mobile, Electronic Arts, Tom Ford, Burberry, and others.
8. Maintain and Evolve the Deployment Over Time
LLMs drift as processes and content change. We handle continuous updates, dataset adjustments, and model refinements so the system stays aligned with your workflows inside the enterprise. With zero staff turnover on active projects, the same experts maintain and optimize your deployment throughout its lifecycle.
Future Trends in Enterprise LLMs
Growing Budgets and Larger LLM Investments
Companies are committing more resources to LLM initiatives. 72% of organizations expect their AI spending to rise, and nearly 40% already invest over $250,000 annually, according to Kong Research’s 2026 Enterprise LLM Adoption Report.
Stronger Preference for Paid, Enterprise-Grade Models
LLMs are moving into critical workflows, driving demand for reliability and SLAs. 63% of enterprises now choose paid versions over free tiers. This signals a market that values stability more than experimentation.
Google’s Expansion in the Enterprise LLM Space
Adoption data shows a shift toward Google’s ecosystem. 69% of enterprises use Google models, compared to 55% using OpenAI. The momentum is driven by Gemini’s integration across Workspace and cloud tooling, reducing friction for companies already using Google infrastructure.
Hybrid Model Architectures Gain Momentum
Enterprises are choosing a mix of proprietary APIs and open-source checkpoints to balance cost and performance. 37% now advocate for hybrid LLM strategies, according to the same Kong Research report. This approach lets teams run lightweight models for internal workloads while reserving premium versions for complex reasoning.
Security and Data Privacy Remain Key Barriers
LLM deployment frequently stalls when sensitive information cannot be isolated from external systems. Instead of expanding access, many organizations redesign their architecture so the model interacts only with pre-approved context retrieved on demand.
Growing Confidence in Open-Source LLMs
For teams that need deeper control, open-source models are becoming the preferred foundation. Their transparency makes it possible to adapt behavior, optimize resource usage, and refine outputs without relying on a vendor’s roadmap.
Clear Priorities for High-Value Enterprise Use Cases
Industry giants gravitate toward use cases that show measurable returns. Customer-facing teams deploy LLMs to speed up case handling and improve the accuracy of responses, while engineering groups use them to remove friction in code generation and documentation. These patterns continue to outperform other categories because the benefits appear quickly and are easy to quantify.
More Openness to Global LLM Providers
Procurement strategies are shifting in enterprise settings as companies test competitive models from international vendors. Performance gains, cost advantages, or language coverage sometimes outweigh concerns about geography. The broader vendor landscape gives teams more room to match model capabilities to specific workloads rather than relying on a single provider.
Cost Pressures Still Shape Deployment Strategy
Budget constraints push organizations to rethink how LLM workloads run in production. Some route everyday tasks through smaller checkpoints, escalating only the most complex prompts to larger models. Others combine retrieval, classification, and summarization pipelines to keep inference volumes under control while maintaining output quality.
A More Positive Workforce Outlook
Teams reporting the highest productivity gains treat LLMs as workflow accelerators rather than replacements. Routine research, summarization, and drafting tasks move faster, allowing employees to focus on judgment-heavy work. This adoption pattern reduces fears of automation and reinforces LLMs as tools that expand capacity, not eliminate roles.
Wrapping Up
Custom LLMs allow enterprises to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and gain invaluable insights from textual data. One of the most compelling applications of LLMs is Generative AI-powered chatbots. These tools offer businesses the opportunity to engage customers in natural, human-like conversations, address queries, and provide tailored product recommendations.
At Master of Code Global, we’ve successfully implemented Generative AI-powered virtual assistants for businesses. The examples include BloomsyBox eCommerce Chatbot and Generative AI Slack Chatbot. These allowed for driving user engagement and automating the knowledge base for employees, respectively.
Beyond AI-powered chatbots, our expertise extends to a comprehensive suite of Generative AI development services. We understand that every business is unique, and its requirements vary. That’s why we offer a customized LLM development solution for enterprise needs that caters to specific industry demands.
With us, you’re not just adopting a technology; you get a strategic tool to boost your customer interactions and drive business growth. Join our LLM development company on this journey to stay ahead in innovation and customer satisfaction.
FAQ
For enterprise use, what are the best LLMs to compare to general-purpose models when accuracy, trust, and usability matter most?
Enterprises typically benchmark against Claude 3 (Anthropic), GPT-4o / GPT-4.1 (OpenAI), Gemini 1.5 Pro (Google), and Cohere Command R+. These models consistently perform well in evaluations involving factual reasoning, compliance-sensitive outputs, and complex instructions.
When domain depth matters, organizations also test LLaMA-3 fine-tunes, Mistral 8×7B, or Mixtral models because they offer stronger control, transparent architecture, and predictable behavior on internal datasets.
Which enterprise LLMs are recommended for high-volume workloads?
Such environments (support automation, document processing, knowledge retrieval) require models that balance quality with cost efficiency.
Enterprises commonly select:
- Cohere Command R / R+ for large-scale inference with stable throughput.
- Mistral 7B / Mixtral 8×7B for on-prem or VPC deployments where cost and latency must stay predictable.
- OpenAI GPT-4o mini / GPT-3.5 variants for scalable API usage with strong performance per dollar.
- LLaMA-3 or custom fine-tuned smaller models when organizations want to run inference internally without per-token costs.
How suitable is Claude for enterprise use?
Claude is one of the strongest enterprise LLMs for tasks requiring safety, reasoning quality, and strict adherence to instructions. Key advantages include:
- High factual reliability compared to many general-purpose models.
- Robust safety architecture grounded in Anthropic’s constitutional AI framework.
- Large context windows, which make Claude effective for long document analysis, RFP summarization, or research-heavy workflows.
- Strong alignment with enterprise governance, as Claude tends to avoid inappropriate or high-risk outputs.
Enterprises often use it for legal review support, policy generation, research summarization, and any workflow requiring consistent interpretability.
Which LLM development companies offer pricing models that support customer loyalty and repeat business?
Master of Code Global supports customer loyalty and repeat business through transparent, milestone-based pricing, predictable monthly support plans, and flexible infrastructure options that prevent vendor lock-in and keep long-term costs under control. Instead of pushing clients toward higher consumption, we prioritize cost-efficient design through prompt optimization, caching, RAG, and model routing. Our engagement model is built for stability: clear project phases, fixed SLAs, and ongoing roadmap collaboration that helps clients expand use cases at a sustainable pace and see continuous value without unexpected spending.
How can enterprises select the most accurate AI language model for reporting?
Reporting workloads require strict factual accuracy and traceability. The best models can distinguish between internal/external enterprise data, pulling only the approved sources into summaries and reports. Enterprises evaluate models using the following:
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) tests to measure whether the model uses verified data rather than hallucinating.
- Ground-truth comparison sets, typically past reports, regulatory filings, or internal dashboards.
- Domain-specific fine-tuning when terminology or compliance rules require precision.
- Hallucination and contradiction benchmarks that measure output stability across multiple prompts.
Models like Claude, Gemini 1.5, and GPT-4o commonly perform best for structured reporting because they follow constraints consistently.
What certifications should enterprises look for in compliant LLMs?
When evaluating LLM vendors or deployments, enterprises typically look for:
- ISO 27001 – Information security management.
- SOC 2 Type II – Controls for data security, availability, and confidentiality.
- HIPAA compliance – For healthcare or PHI workflows.
- GDPR alignment – For EU data handling and user privacy.
- FedRAMP or StateRAMP – For government or public-sector use.
- CSA STAR – Cloud security assurance for third-party infrastructure.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to see how Generative AI chatbots can revolutionize your customer support and boost your company’s efficiency.