This article brings together around 150+ insights from McKinsey, Deloitte, NVIDIA, JAMA, and other trusted sources. Instead of scanning dozens of separate reports, you’ll find the most important numbers collected here, in one place.
The AI in healthcare statistics we highlight cover not just market growth. They show where organizations are already seeing ROI, which use cases look safest to scale, and where the biggest risks and barriers remain.
You can read it from start to finish or jump straight to the section most relevant to your business. Either way, the goal is the same: to give you clear, evidence-based insights you can trust. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
AI in Healthcare Market Size Statistics

Overview & Growth Trends
According to the PrecedenceResearch:
- The AI in healthcare global market size was valued at $26.69 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach approximately $613.81 billion by 2034. This reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.83% over the period from 2025 to 2034.
- North America holds a 45% share, making it the leading region for the adoption of AI in healthcare. Europe follows with 27%, and Asia Pacific accounts for 22%. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa represent smaller portions, at 4% and 2% respectively.
- By component, software leads with a 41% share, followed by hardware at 35% and services at 24%. This dominance underscores the importance of algorithm-driven innovation across clinical and administrative functions.
- In terms of application, medical imaging and diagnostics hold 22.30%, the highest among all categories. The drug discovery and development segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 21.20% through the forecast period.
- By technology, machine learning led with a 39.80% share in 2024, while the computer vision segment is projected to expand the fastest, with a CAGR of 20.70%.
Generative AI in Healthcare Stats
As per the RootAnalysis report:
- The GAI in the healthcare market size is estimated at $3.3 billion in 2025 and forecasted to reach $39.8 billion by 2035, growing at a 28% CAGR.
- A majority of companies in this space (79%) are headquartered in North America, and over 45% are mid-sized firms.
- 8% of organizations are directly involved in drug development, with solution types including technology platforms (87%) and services (18%).
- Key application areas for Generative AI: virtual nursing assistance (50%), patient monitoring and predictive analytics (43%), medical imaging and diagnostics (42%), personalized treatment (33%), and clinical trials (27%). Additional use cases include drug discovery (25%), patient support (22%), clinical judgment (22%), drug design (17%), research (15%), medication manufacturing (8%), and other fields (32%).
- End-user segments are led by healthcare providers (85%), followed by pharma/biotech companies (47%), other stakeholders (25%), and research institutes (17%).
AI in Healthcare Statistics: Investments and Funding
According to Silicon Valley Bank, global venture capital (VC) funding for artificial intelligence in the medical field peaked at $24 billion in 2022, with 132 funds closed. It dropped sharply to $9.7 billion in 2023, but momentum returned in 2024, reaching a projected $16.9 billion.
Investor focus is shifting: administrative automation grew to 42% of all deals, up from 26% in 2019, while clinical AI’s share declined to 32% (from 43–44%). Therapeutics and research remained steady at around 25%.
Within clinical one, patient diagnostics account for 52% of total investment, highlighting strong confidence in analytics, imaging, and testing solutions.
| Group | Area | Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative ($6.6B) | Virtual assistants | $2.6B |
| Notetaking & EHR documentation | $1.6B | |
| Revenue cycle operations | $1.7B | |
| Data structure, analytics & interoperability | $677M | |
| Clinical ($12.5B) | Patient stratification | $687M |
| Patient diagnostics: Analytics & tests | $5.3B | |
| Patient diagnostics: Imaging | $1.4B | |
| Remote monitoring | $1.3B | |
| Therapeutics & Research | Therapeutics & drug discovery | $12.9B |
| Clinical trial enablement | ||
| R&D tools |
Artificial Intelligence Adoption Insights
AI Usage in Healthcare Statistics: General Perspective
According to the NVIDIA Survey, implementation is widespread across the sector:
- 63% of organizations report actively using technology, while another 31% are piloting or assessing projects, showing broad integration.
- The top workloads overall are data analytics (58%), Generative AI (54%), and large language models (53%).
- Healthcare payers and providers rank Conversational AI as their leading workload (54%), reflecting demand for patient-facing solutions.
- Medical tech companies highlight data processing (55%) among their top three, underscoring the importance of structured information management.
Findings from the EY Health Care Executive Survey show high levels of trust and advocacy:
- 96% of executives trust artificial intelligence, with 94% seeing it as a positive force in their workplace and 91% viewing it positively for society overall.
- 95% advocate for its introduction in their business, and 72% mention current GenAI utilization.
- 94% believe intelligentization will improve productivity and efficiency, freeing staff for higher-value tasks.
- Concerns remain: 85% worry about automation in the workplace, with 62% saying this fear has increased since last year. 83% are uneasy about it assisting with diagnoses or personalized medical plans, and 91% emphasize the need for human supervision.
- 88% are comfortable with intelligent systems in hiring, and over half support employing those for tasks such as note-taking, customer queries, data analysis, and forecasting.
- 85% would view organizations more positively if technology usage were transparent, ethical, and responsible.
AI Use in Healthcare Statistics: Applications
According to NVIDIA, adoption is spreading across different segments, each prioritizing distinct workloads and goals.
Overall use cases: medical imaging and diagnostics (47%), clinical decision support (43%), disease diagnosis and risk prediction (40%).
- Medtech, tools, and diagnostics: 71% use AI in medical imaging, 43% in care decision aid, 42% in disease risk forecasting.
- Digital healthcare: decision-making assistance (53%), streamlining operations (47%), and virtual assistants/chatbots (46%).
- Pharma and biotech: drug discovery (59%), genomics (54%), personalized medicine (41%).
- Payers and providers: process optimization (48%), NLP in documentation (44%), medical imaging and diagnostics (43%).
Overall goals: accelerate R&D (24%), improve outcomes (22%), deliver insights (22%).
- Medtech, tools, and diagnostics: raise precision (33%), surface insights (26%), boost outcomes (23%).
- Digital healthcare: drive better outcomes (26%), elicit insights (22%), competitive advantage (22%).
- Pharma and biotech: 54% prioritize accelerating R&D, with 23% citing precision and 22% insights.
- Payers and providers: raise efficiency (29%), attain improved outcomes (26%), and enrich clinician-patient interactions (24%).
A review published in PubMed Central offers a more clinical angle, where the main drivers are caregiver and patient-focused:
- 72% see caregiver burden reduction as the top priority, followed by patient safety/quality (58%) and workflow efficiency (53%). Financial goals are lower: margin improvement (12%) and client experience (5%).
- Key use cases in development: care plan notes (68%), chart summarization (74%), clinical trial automation (50%), care navigation (61%), scheduling (52%), triage (50%).
- In deployment: imaging and radiology (50%), deterioration risk (19%), remote monitoring (21%), in-basket automation (37%), predicting no-shows (17%), utilization review (22%).
- Fully implemented: early sepsis detection (48%), risk of unplanned admission (29%), clinical deterioration (37%), imaging and radiology (40%), in-basket automation (14%), medical coding (24%).
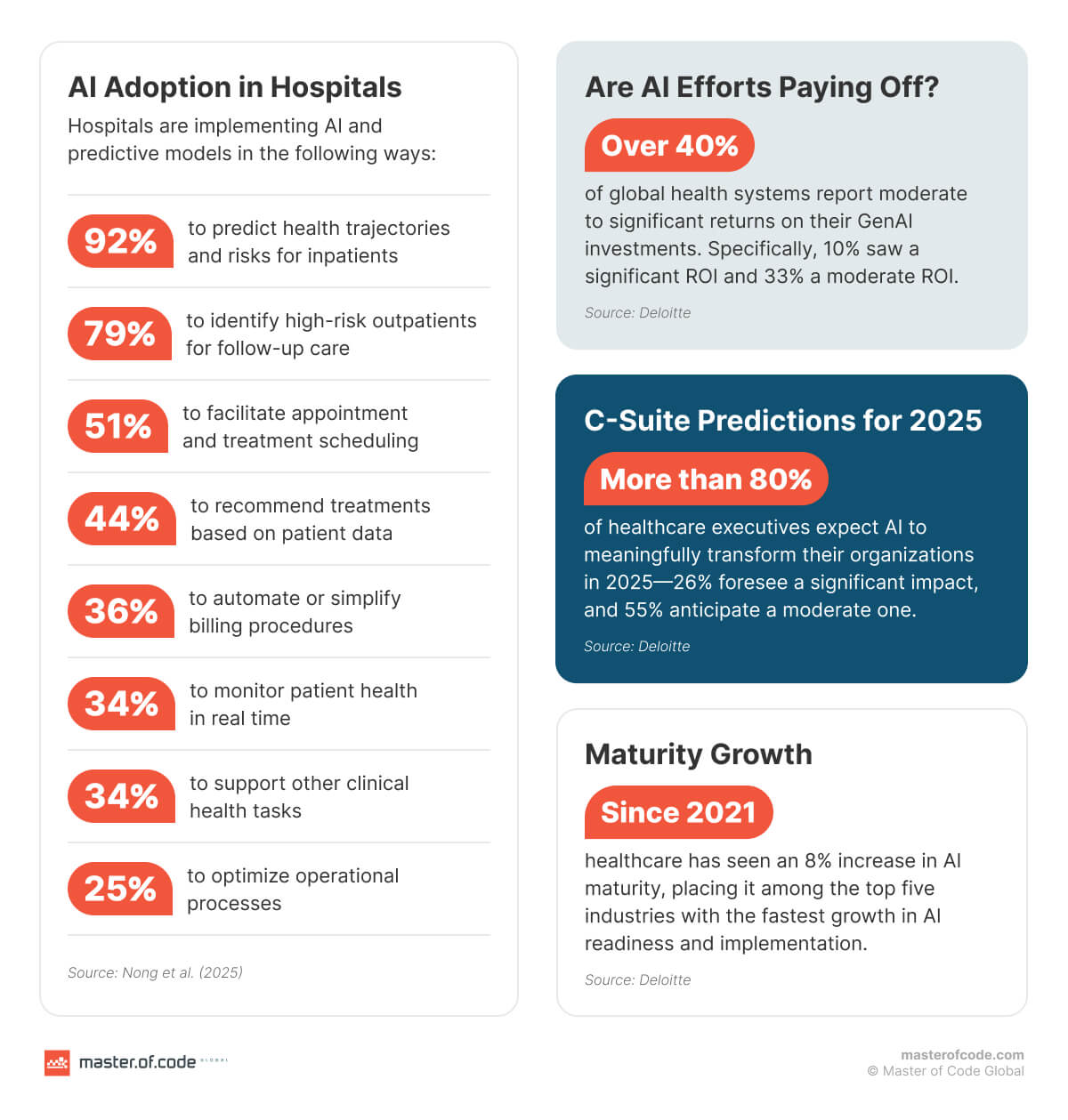
From a hospital perspective, Nong et al. highlight how predictive models are already integrated into operations:
- 92% use AI to predict inpatient health trajectories, while 79% track high-risk outpatients.
- 51% apply it for scheduling, 44% for treatment recommendations, 36% for billing.
- 34% use it for real-time monitoring, 34% for other clinical tasks, and 25% for operational optimization.
Finally, the European Commission’s survey points to what’s already possible with current tools:
- 83% use machine intelligence to optimize resources and workflows, and 74% to streamline administrative tasks.
- 74% see improvements in diagnostic accuracy, while 60% apply smart solutions to personalize treatment.
- Other areas include patient engagement/adherence (43%), predictive analytics (43%), workforce skill gaps (37%), and equitable access (33%).
Generative AI in Healthcare Statistics
According to Deloitte, executives see GAI as a defining factor for strategy:
- 81% identified the proliferation of this technology as a key trend shaping healthcare.
- 72% ranked investment in tech innovations as important or very important.
- Digital transformation was rated impactful by 52% of non-US executives, compared with just 30% of US respondents.
- Most health systems plan to explore or are developing Gen AI use cases over the next 12 months.
- More than 40% already report a significant-to-moderate ROI from their investments, while 37% say it is too early to assess.
The NVIDIA Survey highlights implementation across industry segments:
- Among those utilizing Gen AI, 63% are actively using it, and 36% are piloting or assessing.
- By segment, usage is highest in digital healthcare (71%), followed by pharma/biotech (69%), medical technologies (60%), and payers/providers (44%).
- Top use cases: coding and generating clinical notes (55%), chatbots/agents (53%), and literature analysis (45%).
Insights from McKinsey’s Report confirm broad adoption momentum:
- 85% of organizations have implemented or are pursuing GenAI proofs of concept.
- Overall: 47% already employed, 38% in proof of concept, 12% planning this year.
- By segment: payers (48% integrated, 40% in PoC, 10% preparation), health systems (40%, 40%, 13%), health services & tech (57%, 30%, 13%).
- Areas of greatest potential: administrative efficiency (75%), clinical productivity (74%), patient engagement (55%), IT/infrastructure (55%), quality of care (51%), research/education (41%).
- Segment-specific priorities: payers emphasize admin effectiveness (47%) and clinical throughput (43%), health systems focus on productivity (48%) and service standards (35%), while health services/tech groups lead in adoption with 57% already using it.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare Statistics
Findings from the NVIDIA Survey highlight strong business impact:
- 41% said artificial intelligence accelerated research and development, making it the top-reported benefit.
- 36% cited competitive advantage, while 35% pointed to reduced project cycles, better insights, and enhanced precision.
- 81% of respondents registered increased annual revenue due to artificial intelligence adoption.
- 73% stated it decreased operational costs, improving efficiency and sustainability.
Beyond organizational gains, AI is showing measurable clinical and patient-centered advantages:
- Early disease risk identification. Intelligent models can forecast conditions like cardiovascular disease with 90%+ accuracy years before symptoms appear.
- Personalized treatment plans. AI-driven therapies boost outcomes by 30–35% compared to traditional methods.
- Medication adherence. Advanced forecasting approaches improve dedication rates by up to 30%.
- Diagnostic assistance. Predictive analytics exceeds 90%+ precision across specialties, strengthening physician decision-making.
- Treatment outcome prediction. Smart models predict immunotherapy responses with 70–90% accuracy, reducing trial-and-error in care.
- Workflow optimization. AI can automate up to 30% of administrative tasks, helping providers spend more time with patients.
- Readmission reduction. Predictive EHR models cut rehospitalization rates by 15–20%, saving billions in avoidable costs.
- Hospital-acquired infection prevention. Machine learning can foretell urinary tract infections with 72% accuracy before symptoms emerge, bolstering safety.
- Fraud detection. Autonomous systems are showing strong results, with neural networks improving identification accuracy by 42.7% and cutting false positives by 58.4%. Cost-benefit analyses further show an average ROI of 734% within just two years of implementation.
Statistics on AI in Healthcare Success Areas and ROI
Insights from the European Commission show strong confidence in artificial intelligence for administrative use cases:
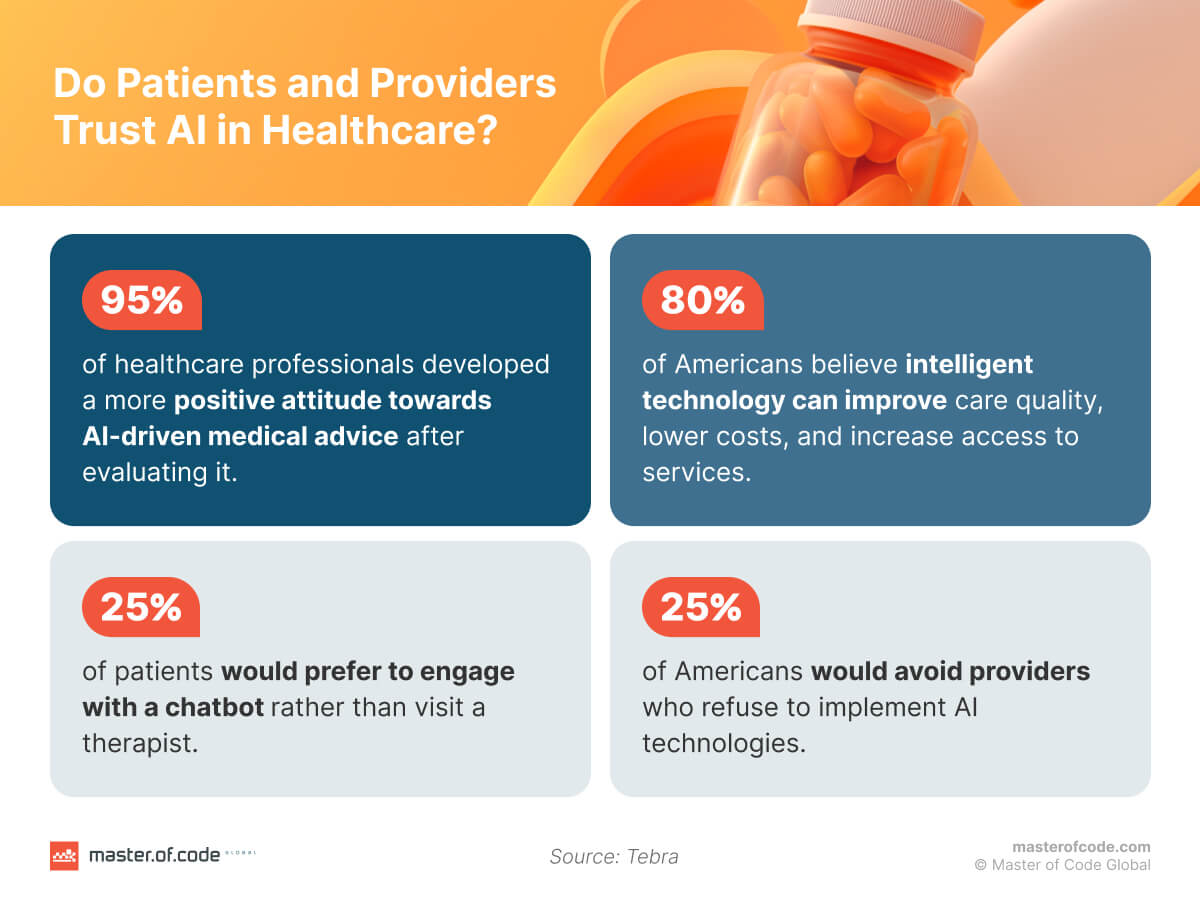
- 71% of healthcare professionals and 87% of hospital representatives highlighted tools such as large language models and NLP as the most transformative.
- 83% of patients also noted being comfortable with their usage in medical settings.
Findings from PubMed Central’s publication highlight where AI has already delivered measurable results:
- Clinical documentation (53%) leads as the most successful use case.
- Risk stratification (38%) is also widely recognized.
- Revenue cycle management shows notable progress at 23%.
- Other areas reporting gains include automated analytics (19%), diagnosis (19%), and business functions outside the revenue flow (16%).
The NVIDIA survey revealed that Generative AI is already paying off. 45% of organizations using it reported returns on investment within the first year of deployment.
According to McKinsey, ROI from GAI varies significantly across healthcare segments:
| ROI Category | Overall (%) | Payers (%) | Health Systems (%) | Health Services & Tech (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >4× ROI | 4 | 8 | 4 | 0 |
| 2–4× ROI | 15 | 21 | 10 | 12 |
| <2× ROI | 4 | 4 | 3 | 6 |
| Positive ROI (unquantified) | 41 | 33 | 52 | 36 |
| Negative ROI | 10 | 13 | 0 | 23 |
| Unclear value | 26 | 21 | 31 | 23 |
AI in Healthcare Statistics and Insights on Patient Attitudes
According to a survey published on JAMA Network Open on perceptions of artificial intelligence in the medical field, we identified the following key insights.
General Attitudes
- 57.6% of patients had positive views of this technology in medicine, and 62.9% favored its growing use.
- Female respondents were less optimistic (55.6%) compared to males (59.1%).
- Patients in very poor health were most dismissive: 26.6% extremely negative and 29.2% rather unfavorable. Among those in very good health, only 1.3% and 5.3% shared those thoughts.
- AI knowledge strongly shaped opinions: 83.3% of experts were favorable, versus just 38.0% of patients with no proficiency.
Trust in Artificial Intelligence
- 48.5% trusted AI to enhance healthcare, while 43.9% authorized it for reliable health information, and 43.6% for accurate diagnoses.
- 41.8% relied on it to assess therapy response.
- Confidence was higher among men (51.4%) than women (45.0%).
- 77.3% of AI experts counted on technology to improve care, compared to 35.9% with no knowledge.
- When asked about conditions, 11.4% opposed it entirely, 27.9% accepted it for minor illnesses, 26.7% for moderate, and 34.0% for severe.
- 42.9% depended on highly accurate algorithms for vital decisions, rising to 50.4% among very healthy patients vs. 26.0% among very ill ones. Among experts, trust was 91.4% compared with 36.0% for those with no proficiency.
Preferences Toward AI in Healthcare Facilities
- 62.0% favored institutions using artificial intelligence for diagnosis, and 71.4% often or always chose places that employ this tech.
- Men were more positive than women: 63.9% vs. 59.9% (diagnosis), and 73.7% vs. 68.7% (facility use).
- AI experts were much stronger advocates. 79.7% preferred forward-thinking facilities vs. 46.2% of those with no knowledge.

AI in Diagnostics
- 59.3% supported intelligent solutions for radiograph analysis, 54.6% for cancer diagnosis, and 67.9% for use as a second opinion.
- 70.2% preferred explainable intelligence even if less accurate than black-box models.
- 46.5% favored sensitivity over 36.3% choosing specificity.
- 72.9% advocated joint physician-AI diagnosis, with doctors making the final decision.
- Only 4.4% championed fully autonomous systems, while 6.6% preferred physicians diagnosing without tech usage.
Concerns about Intelligentization
- 53.2% worried about data protection.
- 61.8% feared reduced physician–patient interaction, and 61.7% dread physician replacement by machines.
- 57.4% were concerned about rising healthcare costs.
- Uncertainties were lower among AI experts: 52.2% vs. 62.2% (replacement fears), and 51.7% vs. 62.6% (cost concerns).
Challenges and Regulations of AI in Healthcare Statistics
The Deloitte report shows both optimism and caution:
- More than 80% of executives expect Generative AI to have a moderate (55%) or significant (26%) impact on their organizations in 2025.
- Respondents also emphasized that regulatory oversight is necessary to safeguard patient safety.
- In the United States, HIPAA compliance remains a critical consideration for any AI tool handling patient data, ensuring privacy and security alongside FDA oversight.
- In Europe, the EU AI Act applies to all intelligent systems placed on the EU market, categorizing them as unacceptable, high, limited, or minimal risk. Inappropriate solutions are prohibited and must be phased out.
The NVIDIA survey highlights technical and resource-related obstacles:
- 33% cited data issues, such as privacy and sovereignty, as the biggest challenge.
- 30% pointed to limited budgets, while another 30% reported insufficient data sizes for model training.
Findings from PubMed Central’s article reveal additional barriers to adoption:
- 77% cited lack of AI tool maturity as the single most pressing obstacle.
- Financial concerns were raised by 47% of respondents, and 40% noted regulatory or compliance uncertainty.
- Other issues include limited clinician adoption (17%), lack of in-house expertise or technology (14%), and weak leadership support (7%).
Real-World Examples of AI in Care
In addition to theoretical statistics of artificial intelligence in healthcare industry, let’s look at real success stories from the field.

- Johns Hopkins University Hospital introduced tools that support rounds, analyze records, and schedule appointments. They cut ER bed assignment times by 30%, reduced OR transfer delays by 70%, and shortened ambulance response times by 63 minutes.
- At Mid and South Essex NHS Trust, an AI pilot lowered patient no-shows by 30% in six months. This enabled 1,910 additional patients to be seen and prevented 377 missed appointments.
- A US hospital using the Holistic AI in Medicine framework boosted length-of-stay prediction accuracy from 8% to 20%. It also improved the 48-hour mortality projection from 11% to 33%, strengthening clinical decision-making.
- The CSource cancer support chatbot, redesigned by Master of Code Global, served over 1,500 users across 89 cancer types, offering a trusted hub for quick answers and expert-reviewed content.
- A Canadian insurer’s AI-powered prescription management app cut medication-related support calls by 43%, securely processed over 1 million records, and expanded its drug database by 320%.
- A Southwest US healthcare provider deployed an intelligent triage assistant. It facilitated a reduction in wait times by 63% and abandoned calls by 47%, as well as achieved 89% patient satisfaction with interactions.
- MIT researchers used an advanced algorithm to identify a new class of antibiotic candidates in just 48 hours, accelerating drug discovery through deep learning.
- At UnityPoint Health, AI cut readmissions by 40% in 18 months. At the University of Kansas Health System, it decreased diabetes readmissions from 25% to under 14%, while Flagler Hospital lowered pneumonia-related rehospitalizations from 2.9% to 0.4%.
- Intelehealth, supported by Johns Hopkins, uses machine intelligence to guide community workers in remote areas, helping deliver care to over 12 million people.
- Seha Virtual Hospital connects 224 facilities, enabling 1.6 million virtual visits and supporting 255,000 patients through AI-enabled consultations and screenings.
- CSL (Australia’s largest biopharma) applies artificial intelligence for drug development and patient stratification, leveraging biomarkers to accelerate precision medicine.
- TPMG’s AI scribe program saved 15,700 hours of physician documentation across 2.5 million visits, with 84% of doctors reporting better patient connection.
- Cencora integrated a voice-based agent that manages insurance calls 4× faster than staff, freeing capacity equivalent to 100 full-time employees.
Future of AI in Healthcare Statistics
Hospital leaders surveyed pointed to areas where artificial intelligence could deliver the most transformative impact:
- 88% expect administrative support tools to be the most impactful.
- 66% see value in clinical workflow optimization, and another 66% in remote monitoring.
- 59% cited AI-assisted diagnostics.
- 56% expect conversational platforms for patient assistance to grow in importance.
- 47% believe in prognosis prediction (risk stratification).
- Lower-ranked but emerging areas include AI-assisted symptom checkers (28%) and medical robotics for surgery (25%).
The NVIDIA Survey underscores this optimism:
- 86% of respondents said AI is important to their organization’s future, and 83% agreed it will revolutionize healthcare within 3 to 5 years.
- Medtech, telemedicine, tools, and diagnostics: 75% expect advanced medical imaging to lead, followed by virtual assistants (VA) (31%) and precision medicine (20%).
- Digital healthcare: cutting-edge imaging (48%), chatbots (40%), targeted therapy (37%).
- Pharma and biotech: advanced imaging (48%), VA (40%), precision medicine (37%).
- Spending priorities: 47% plan to identify new use cases, 34% will focus on workflow and production optimization, and 26% aim to hire more experts.
Conclusion: AI in Healthcare Statistics and the Road Ahead
The data shows that technology has moved from pilot projects to large-scale use across the medical field. Market growth is accelerating, investments are rising again, and hospitals, pharma, and insurers are already reporting measurable improvements in diagnostics, workflows, and patient access.
At the same time, artificial intelligence in healthcare statistics reveals important caveats. Adoption depends not only on financial backing but also on tool maturity, regulatory clarity, and trust among clinicians and patients. These challenges are shaping the pace and scope of implementation as much as technological capability itself.
What stands out is that organizations already applying the tech are achieving tangible results, from faster decision-making to cost savings and better patient outcomes. For those still assessing their options, the numbers suggest that waiting carries a risk of being left behind.
The numbers show clear opportunities for impact. Through healthcare AI consulting, we help businesses put them into action. Ready to book a slot?





