We’ve entered an era where data is the new currency, and businesses are grappling with the challenge of processing massive chunks of information. This effort is vital for informed decision-making, enhanced customer satisfaction, and business growth.
In light of this, questions arise: Is your company equipped to manage extensive data sets and analytics? Are the tools at your disposal effective enough? Addressing these questions highlights one game-changing innovation: integrating Generative AI in data analytics.
Read our article to learn how Generative AI can transform your business intelligence (BI) while enhancing your strategic decisions and fostering further expansion.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Generative AI for business intelligence closes a major adoption gap: with only ~26% of organizations actively using BI tools, natural language and AI-driven insights bring analytics into everyday decisions.
- As global data volume reaches 181 zettabytes by 2025, traditional BI falls behind. Generative AI automates analysis and explanation, addressing the 67% of executives who struggle to use existing BI tools effectively.
- The payoff is tangible. About 65% of companies report improved decision quality with AI-augmented BI, and over 60% of marketing and sales teams already rely on AI to analyze performance and customer signals.
The Evolution of Business Intelligence: From Static Reports to AI-Enhanced Interfaces
For decades, BI focused on describing the past. Companies relied on dashboards that summarized yesterday’s or last month’s performance. These delayed outputs forced leaders to react after trends had already shifted: a serious handicap in today’s competitive environment. Today, only ~26% of organizations actively use BI tools, highlighting how slow traditional adoption has been at the operational level.
The real change began with augmented analytics, a term Gartner popularized to describe BI platforms that embed AI and machine learning to automate data preparation, pattern detection, and insight generation. These capabilities help uncover trends that static dashboards miss and reduce manual effort. Demand for these AI-driven analytics is growing quickly: analysts project the augmented analytics market will expand at about a 21.8% compound annual growth rate through 2033.
AI has also begun reshaping how decisions are made. Surveys indicate that around 80% of firms treat data as critical for decision-making. Early results from AI-augmented BI adoption are promising too, with about 65% of companies reporting improved decision quality when AI tools help surface trends and anomalies that humans might overlook.
The most significant leap is predictive and prescriptive intelligence. Traditional BI answers what happened; today’s AI-enhanced platforms help explain why it happened and forecast what could happen next, enabling scenario planning and strategic choices in real time.
The result? Decisions that once took weeks now happen in hours, freeing leaders to act when it matters most. This evolution turns Generative AI for business intelligence from a rear-view mirror into a forward-looking engine of strategic growth, and it sets the stage for how GenAI will accelerate every step of that journey.
How Crucial Is AI for Business Intelligence Today?
Data-driven organizations consistently outperform their peers, but the gap is no longer explained by access to data alone. What separates leaders is how quickly and effectively they turn data into decisions. As volumes grow and complexity increases, traditional BI approaches are reaching their limits.
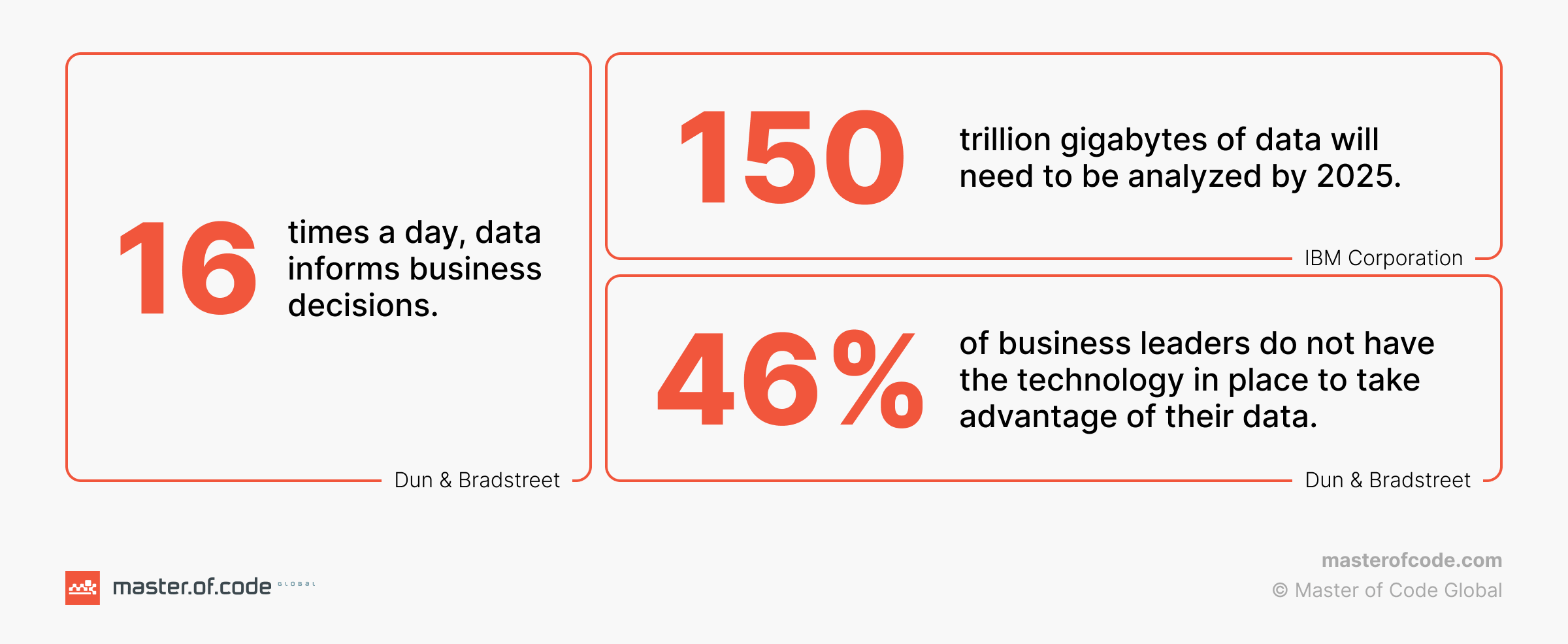
The scale of the challenge is hard to ignore. Global data creation is projected to reach 181 zettabytes by 2025, according to IDC, driven by digital transactions, connected devices, and customer interactions. Effectively managing and utilizing this vast amount of information is becoming increasingly essential. Nevertheless, 67% of executives struggle with using existing tools to access and utilize information.
This is where AI becomes critical for modern Generative business intelligence. Manual dashboards and static reports cannot process data at this scale, nor can they surface insights fast enough for operational or strategic use. AI-driven BI systems automate data preparation, detect patterns humans miss, and surface explanations instead of raw metrics.
Generative AI adds another layer of impact. In functions like marketing and sales, more than 60% of professionals already use AI to analyze performance data and customer signals. This accelerates insight discovery and reduces reliance on specialized analysts. Instead of waiting for reports, teams can ask questions in natural language and explore answers in real time.
Generative BI vs. Generative AI
One generates content; the other generates insight grounded in business data.
Generative AI is a general-purpose capability designed to produce text, code, images, or summaries. BI applies those same models inside analytics environments, where outputs are constrained by enterprise data, metrics, and governance rules.
| Dimension | Generative BI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Primary purpose | Explain datasets and support decisions | Generate content |
| Core focus | Metrics, KPIs, trends, anomalies | Language, code, images, multimodal output |
| Input data | Structured enterprise data | Prompts, documents, mixed inputs |
| Output | Explanations, forecasts, scenario insights | Text, summaries, code, creative assets |
| Interaction | Business questions in natural language | Open-ended prompts |
| Data grounding | Strong, tied to internal systems | Optional unless explicitly constrained |
| Decision impact | Direct and operational | Indirect |
| Typical users | Executives, managers, analysts | Broad employee base |
| Risk profile | Lower with proper data grounding | Higher without guardrails |
How Generative AI Is Used in Business Intelligence
Data Collection
Think of Alex, a revenue operations lead at a mid-sized SaaS company. Every morning, data arrives from CRM, billing, product usage, marketing tools, and support tickets. None of it speaks the same language.
With Generative AI embedded in BI, Alex doesn’t manually map fields or reconcile formats. The system:
- Interprets schemas automatically;
- Flags missing or inconsistent records;
- Explains gaps in plain language.
Instead of asking “Why is this column empty?”, Alex gets “Usage data from Segment stopped syncing at 02:15 UTC.” The process shifts from detective work to oversight.
Data Analysis
Now, imagine Alex notices a revenue dip. Traditional BI shows the decline. That’s it.
The application of AI in BI goes further. It analyzes patterns across datasets and explains relationships:
- Which customer segments changed behavior;
- What events preceded the shift;
- Which variables correlate strongly, and which don’t.
Alex asks: “Why did MRR drop last week?” The system responds with a ranked explanation, not a dashboard maze. Analysis becomes conversational, not interpretive.
Data Visualization
Next, Alex needs to brief leadership fast. No time to design charts or adjust filters. With Generative AI, Alex says: “Create a view showing weekly churn by plan, with annotations for pricing changes.”
The BI interface generates the visualization automatically:
- Chooses the right chart type;
- Highlights anomalies;
- Adds context directly to the visual.
Instead of tweaking dashboards, Alex focuses on the story the data tells.
Action Planning
Finally, Alex needs to act. Insights without decisions stall.
Generative AI closes the loop by supporting scenario thinking:
- “What happens if we adjust pricing for this segment?”
- “Which customers should sales prioritize this week?”
- “What actions reduced churn in similar situations?”
The system simulates outcomes based on historical data. Action planning moves from gut feeling to evidence-backed choices.
Generative AI Use Cases in Business Intelligence
The versatility of AI in data-driven environments is increasingly evident. Below are six practical use cases that show how it supports Generative business intelligence workflows, from insight discovery to decision support.
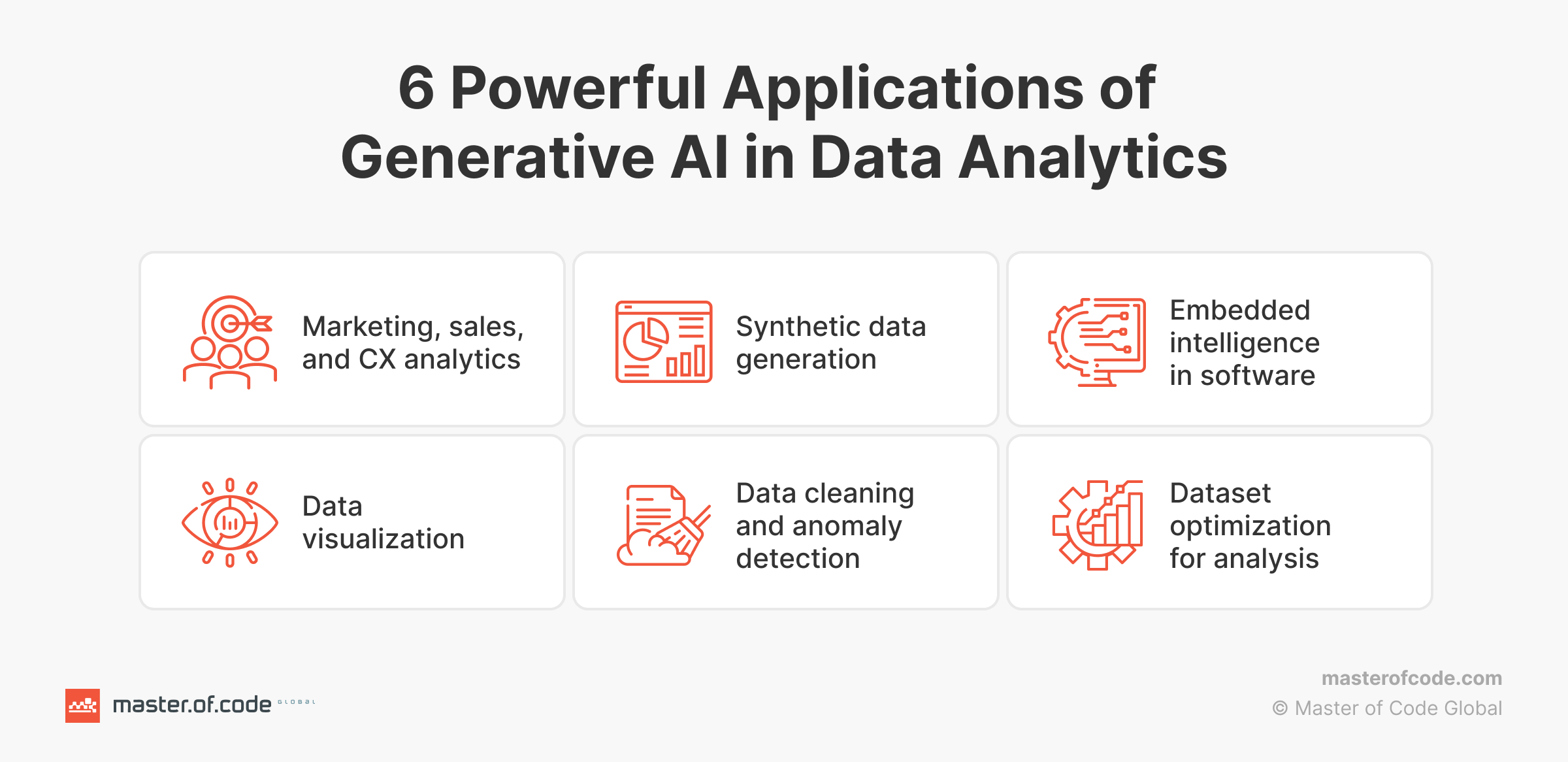
Marketing, Sales, and Customer Experience (CX) Analytics
By analyzing social media, the technology uncovers emerging consumer preferences and market sentiments. These insights are pivotal in enabling businesses to refine their marketing strategies.
Enhanced understanding of market dynamics helps to create more targeted and effective campaigns. They resonate better with the intended audience. Similarly, Generative AI in sales aids in forecasting trends by interpreting past entries and current market signals. The tool guides businesses toward smarter, data-driven planning and resource allocation.
In the realm of customer experience, Generative AI provides a deep dive into clients’ feedback and interactions. By analyzing this information, businesses can identify key factors that influence consumer satisfaction. This includes analyzing call center interactions and online reviews. The insights gained are used to improve product offerings and customer service strategies.
Moreover, Generative AI in BI enables the personalization of user interactions. This is achieved by understanding individual preferences and behaviors. As a result, businesses can offer more tailored experiences. This approach not only enhances clients’ satisfaction but also fosters loyalty.
Synthetic Data Generation
According to a recent Gartner report, 60% of business leaders are adopting AI-generated data to address real-world materials accessibility challenges. This shift primarily aims to resolve information complexity and availability issues.
Data crafted by AI fills crucial gaps in real-world sources, thereby enhancing model outcomes. A majority of organizations now utilize either partly synthetic data (63%) or a combination of partially and fully artificially generated information (20%). These strategies led to notable improvements in model accuracy (60%), efficiency (56%), and data privacy (45%).
This technology is transforming how industries like finance, healthcare, and marketing tackle data challenges. Generative AI enables the creation of accurate materials. It mirrors real-world intricacies while ensuring info privacy.
For instance, in healthcare, AI-generated synthetic patient records facilitate research without risking privacy. In finance, synthetic transaction data aids in developing fraud detection models without using sensitive details.
The diversity of data types generated by artificial intelligence underscores its wide applicability. Quality assurance is key, as it significantly affects model accuracy and analysis outcomes. To ensure high-quality synthetic data, 65% of organizations reported using multiple information sources for generative models.
This approach is coupled with thorough validation and quality checks. Such a strategy is essential for training machine learning models. The dependability of data directly influences AI applications’ efficacy and reliability.
Embedded Intelligence in Software
AI for BI boosts user interaction and data comprehension in office and enterprise software. Tools such as Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Power BI are now being enhanced with AI assistants. The software provides natural language explanations of datasets within these applications. This integration simplifies understanding complex information, enabling quick and intuitive insights.
AI assistants also aid in generating visualizations, making raw data accessible and actionable. This integration, facilitated by LLM Orchestration Frameworks, like LOFT or LangChain, democratizes analytics, simplifying workflows across various professions.
Ready to enhance your business with Generative AI? Start building your AI solution today and bring your business to a new level!
GET IN TOUCH
Data Visualization
With today’s overwhelming data volumes, identifying key insights for visualization is a challenge. Generative AI automates this process, selecting relevant information and the best visualization type. It even generates the visuals itself, ensuring accuracy and relevance. This automation saves time and simplifies working with large datasets.
AI also adapts to audience preferences, creating engaging, easy-to-understand visuals. By using artificial intelligence, visualization becomes more efficient and insightful. It condenses complex information into accessible formats, essential in today’s data-rich environment. Whether it’s creating user-friendly charts or integrating with digital tools, the technology enhances visualization, making information comprehensible to a wider audience.
Data Cleaning and Anomaly Detection
Virtual assistants excel in identifying patterns and deviations in large datasets and pinpointing errors. They can enhance medical diagnostics, as well as fraud detection in financial transactions.
Moreover, in the domain of natural language processing, Generative AI refines data quality by crafting contextually accurate text for chatbots. It suggests replacements for flawed or missing data, crucial for maintaining its integrity.
Especially useful in complex systems like customer information management, this technology ensures the accuracy of the output. The diverse application of Generative AI in data analysis not only increases the efficiency of database cleaning processes but also substantially improves the reliability and efficacy of its interpretation.
Dataset Optimization for Analysis
AI processes and restructures raw data, making datasets more suitable for in-depth analysis. This optimization is crucial across various fields, from marketing analytics to scientific research.
The quality and structure of information profoundly influence analytical outcomes. Generative AI not only speeds up the analytical process but also reveals deeper insights. This leads to more informed and strategic business decisions.
Top Applications of Generative AI in Business Intelligence
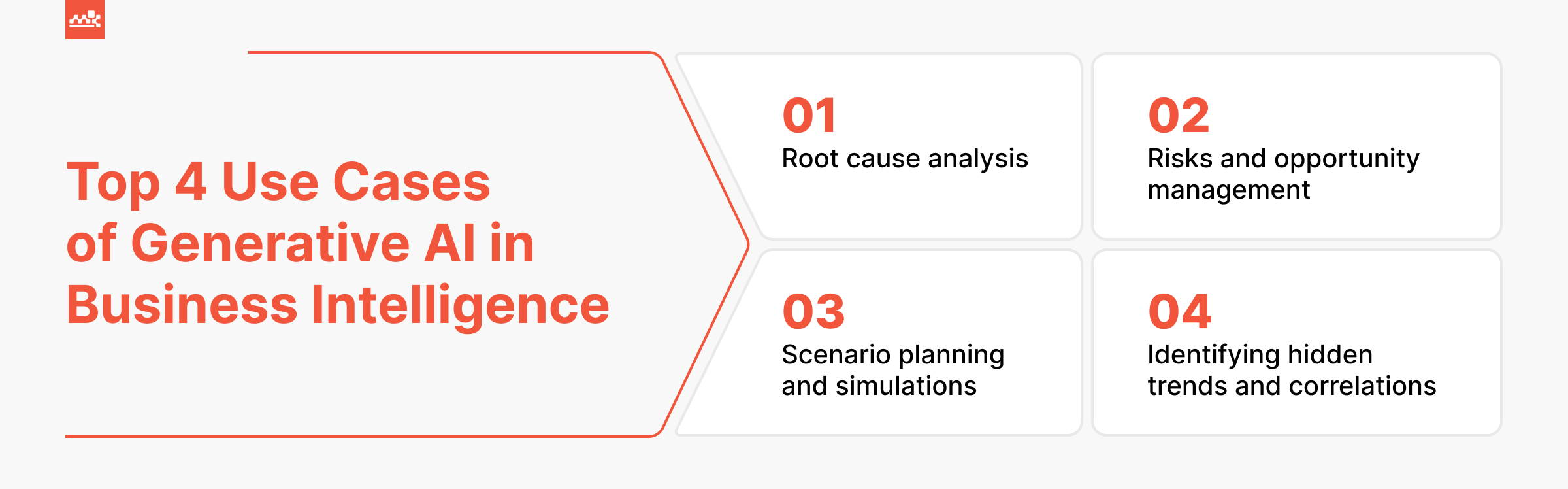
Risks and Opportunity Management
Gen AI models revolutionize risk management by analyzing vast amounts of both internal and external data. This includes news feeds, regulatory filings, financial reports, social media activity, and more. The model’s ability to process information at this scale allows it to pinpoint emerging risks with remarkable speed.
These challenges might include supply chain bottlenecks, shifts in consumer behavior, or even increasing cybersecurity threats. With foresight, companies can proactively develop mitigation strategies. Such an approach enables them to minimize disruptions and protect the bottom line.
On the opportunity side, Generative AI uncovers hidden market trends, potential partnerships, or untapped customer segments. By examining the gathered records, the model can spotlight areas with high growth prospects. Organizations get valuable data that informs strategic decision-making. As a result, businesses gain a clear edge, allowing them to outpace the competition and capture new markets.
Scenario Planning and Simulations
GAI empowers businesses to model complex “what-if” scenarios with unparalleled detail and sophistication. By feeding the algorithm a combination of historical data, demand forecasts, and other relevant variables, companies can simulate a vast range of probable outcomes. AI takes into account dynamic market forces, competitor actions, and even possible disruptions.
This allows firms to thoroughly stress-test strategies, exposing potential weaknesses or hidden risks. Organizations can confidently experiment with different approaches within a simulated environment. They gain valuable insights into resource allocation and risk mitigation before committing capital or making significant strategic shifts.
Thus, with the power to visualize the future, businesses can make more informed decisions. They adapt quickly to changing circumstances and seize opportunities with greater confidence.
Root Cause Analysis
Generative AI serves as a powerful tool for diagnosing problems and unexpected trends. It rapidly analyzes diverse data sources, including equipment logs, user feedback, and production records. The model uncovers hidden correlations and anomalies that would be difficult for humans to detect.
Examples of insights it might reveal include subtle process inefficiencies, overlooked customer pain points, or emerging vulnerabilities within the system. By swiftly identifying root causes, businesses take focused actions. Companies minimize downtime, improve buyer satisfaction, and proactively address potential risks. This translates to reduced costs, enhanced operational resilience, and a stronger overall CX.
Identifying Hidden Trends and Correlations
Intelligent systems excel at spotting subtle patterns and unexpected relationships within large datasets. This capacity allows businesses to anticipate shifts in markets, customer preferences, and even evolving industry landscapes.
By uncovering these early signals of change, companies gain a significant competitive advantage. They can proactively adjust offerings to stay ahead of the curve, ensuring products and services remain relevant. Marketing campaigns become laser-focused, resonating with emerging client segments and maximizing their impact.
Additionally, internal operations can be streamlined in anticipation of future demands, increasing efficiency and positioning the business for long-term success. Ultimately, GAI grants enterprises the foresight to thrive in a constantly changing environment.
Natural Language Interaction
Think of Maria, a regional VP, opening a BI tool five minutes before an exec meeting. Instead of drilling through dashboards, she types: “Why did churn increase in EMEA last quarter?” The system responds with a ranked explanation, grounded in live business data.
This interaction model is gaining traction fast. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 70% of analytics users will rely on natural language interfaces instead of manual exploration, up from less than 20% today. By removing the need for technical query skills, BI becomes accessible at the moment decisions are made.
Automated Content Creation
Every reporting cycle used to end the same way: analysts exporting charts, rewriting insights, and tailoring slides for different audiences. Generative AI changes that last mile.
Analytical outputs are now translated automatically into summaries, performance briefs, and stakeholder-ready narratives. McKinsey estimates that Generative AI can automate up to 60–70% of time spent on data interpretation and reporting tasks, significantly reducing cycle time. For BI teams, this means insights move faster and with less distortion across the organization.
Enhanced Data Storytelling
Numbers rarely persuade on their own. What changes minds is context.
Generative AI stitches metrics into narratives that explain how trends unfold and why they matter. Instead of presenting isolated KPIs, BI outputs describe cause-and-effect relationships across time, regions, or customer segments.
According to Salesforce research, 79% of business leaders say data storytelling improves decision confidence, particularly in cross-functional discussions.
Automated Analytics
Think of a BI team reviewing weekly performance after a quiet dip in conversion rates. The numbers are there, but the moment to act has already passed. No one thought to look sooner, and no alert was waiting.
With Generative AI in place, analytics no longer waits for a question. As new data arrive, patterns are continuously evaluated. Sudden shifts, unusual combinations, or early warning signals surface on their own, long before they harden into problems.
In Generative business intelligence, timeliness often outweighs perfection. Acting on an early signal, even an imperfect one, can prevent losses that hindsight never recovers.
Data Optimization & Synthesis
Picture a strategy meeting where finance, operations, and customer teams bring conflicting numbers to the table. Each dataset is correct in isolation, yet none tell the full story.
Generative AI resolves this by reconciling fragmented inputs into a unified analytical view. It aligns formats, resolves inconsistencies, and connects related data points across systems so analysis reflects how the business actually operates.
When inputs improve, outcomes follow. Clear, consistent data doesn’t just support better models – it supports better decisions.
Code & Task Automation
Behind every polished dashboard is a layer most stakeholders never see: queries rewritten, pipelines adjusted, transformations maintained. For analytics teams, this invisible work consumes more time than insight generation itself.
GenAI absorbs much of that burden. Routine queries are drafted automatically, transformations adapt as data changes, and workflows adjust without manual intervention. Analysts spend less time maintaining infrastructure and more time interpreting results.
As analytics demand grows, productivity no longer depends on adding complexity. It depends on removing it.
Applications of Gen AI in Business Intelligence Across Industries
Financial Services
Banks don’t struggle with data volume; they struggle with interpretation under pressure. Risk teams face streams of market movements, internal exposures, and regulatory signals that change faster than reports can be produced.
At JPMorgan Chase, a combination of Gen AI and BI is applied to interpret these signals together rather than in isolation. Public materials describe how machine learning supports risk analysis, trading insights, and scenario evaluation by connecting market data with internal performance indicators.
The BI value here isn’t automation for its own sake. It’s the ability to reduce uncertainty early, before volatility becomes loss.
Retail
BI used to answer questions after the fact: what sold, what didn’t, what ran out. That lag is costly when margins are thin and demand shifts weekly.
Walmart approaches this differently. Its analytics teams use AI and large-scale data systems to interpret demand signals across stores, digital channels, and supply chains simultaneously. Public disclosures highlight how these insights guide inventory placement, pricing, and merchandising decisions.
Instead of reacting to missed demand, planners focus on anticipating it, turning BI into an operational steering mechanism rather than a reporting tool.
Healthcare
Decisions in complex service environments rarely optimize a single metric. Improving speed, cost, or capacity in one area often creates pressure somewhere else.
At Mayo Clinic, BI fueled by AI is used to synthesize clinical, operational, and administrative data into unified views. Public sources describe how these insights help leaders understand trade-offs between staffing levels, patient flow, and care outcomes. Instead of scanning disconnected dashboards, decision-makers evaluate how changes ripple across the entire system. In BI-driven environments like this, context matters as much as accuracy.
Manufacturing
What if equipment failure could be understood before it happened, not just detected afterward?
That question underpins how Siemens applies AI-driven analytics in manufacturing environments. Siemens describes using advanced solutions to correlate sensor readings, maintenance logs, and production data, helping teams understand emerging issues earlier.
For plant managers, BI moves from retrospective performance tracking to forward-looking operational insight, changing maintenance from reactive response to planned intervention.
Key Benefits of Using Generative AI for Business Intelligence
Improving the Adoption of Business Intelligence Tools and Practices
A sales leader opens a BI tool moments before a forecast meeting, fully expecting friction. In the past, the interface required knowing where to click, which filter to apply, and how to interpret unfamiliar charts. This time, they ask a plain question and receive a clear, data-backed explanation.
That single interaction reshapes behavior. When business intelligence tools respond in natural language and explain why numbers change, they stop feeling like specialist software. They become part of daily work, used by managers and executives without hesitation.
Generative AI tools lower the psychological and technical barriers that have long limited BI adoption. Instead of forcing users to learn the tool, the tool adapts to the user. Over time, analytics moves out of isolated teams and into everyday decision-making, where it has the greatest impact.
Enhancing Business Intelligence Outcomes
An operations director notices margins tightening in one region. The dashboard shows the decline clearly, yet the real question remains unanswered: what changed, and what should be fixed first? In traditional BI, that gap often leads to meetings, follow-ups, and delayed action.
With Generative AI in place, analysis moves beyond surface metrics. The system connects cost fluctuations, supplier performance, demand shifts, and operational constraints into a single explanation. Instead of debating interpretations, teams focus on decisions.
This change improves outcomes because actions are grounded in causality, not correlation. Generative business intelligence stops being a mirror of past performance and becomes a guide for what to do next, helping organizations respond faster and with greater confidence.
Addressing Data Science Skills Shortages
In many organizations, analytics doesn’t fail because of missing data or weak tools. It stalls because too few people know how to move from raw information to insight. Requests pile up, dashboards wait for refinement, and simple questions turn into multi-day tasks.
GAI changes how this bottleneck forms. Analytical reasoning that once required advanced modeling skills is embedded directly into BI workflows. Business users explore data, test assumptions, and interpret results without waiting for specialist support.
The impact is structural. Data scientists stop being gatekeepers and become enablers, focusing on complex modeling, governance, and quality. At the same time, the organization produces more insights with the same talent base, easing skills shortages without lowering analytical standards.
Analyzing Larger Volumes of More Complex Data
Data used to arrive in batches. Now it flows continuously, from applications, devices, customers, and operations, often in different formats and at different speeds. For many teams, the challenge is no longer collecting information, but keeping up with it.
AI absorbs that complexity by examining multiple data streams at once and tracking how patterns evolve over time. Instead of forcing analysts to manually combine signals, the system highlights what actually changed and why it matters. As data volumes grow, insight remains timely, allowing decisions to keep pace with the business rather than lag behind it.
Reducing the Cost of BI Efforts
Budgets for BI rarely depend on infrastructure alone. They accumulate quietly through repeated queries, manual report updates, and hours spent explaining the same results to different stakeholders. Explanations are generated automatically, analyses adjust to new questions without rework, and routine maintenance fades into the background. The same BI stack produces more value with fewer manual steps, lowering the cost of insight delivery without sacrificing depth or accuracy.
Risks and Challenges of Generative BI: What You Should Watch For
Transparency and Explainability
Challenge:
Generative BI systems can produce confident, well-written explanations without clearly showing how conclusions were reached. When stakeholders can’t trace logic back to data, trust erodes, especially in regulated or high-stakes decisions.
How to address it:
At Master of Code Global, we design for traceability from day one. We ensure every generated insight can be linked to underlying data sources, metrics, and assumptions. We also favor systems that expose reasoning steps and allow users to drill into “why,” not just “what.”
Data Security and Privacy
Challenge:
Conversational BI interfaces often pull data from multiple systems at once. Without strict controls, sensitive financial, customer, or employee data can surface in the wrong context or to the wrong user.
How to address it:
We apply role-based access, data masking, and environment separation before enabling generative features. Our team treats Generative BI as an extension of the data perimeter, not a standalone tool, and align it with existing security and compliance policies.
Hallucinations
Challenge:
Generative models can fill gaps with plausible-sounding but incorrect explanations. In BI, even a small hallucination can send teams chasing false trends or making flawed decisions.
How to address it:
At Master of Code Global, we ground generation strictly in verified enterprise data. We use retrieval-based approaches, validation checks, and confidence indicators to distinguish facts from inference. When certainty is low, the system should say so explicitly.
Ineffective Data Architectures
Challenge:
Generative BI amplifies whatever data foundation you give it. Fragmented pipelines, inconsistent definitions, or poor-quality inputs lead to misleading outputs, faster than ever.
How to address it:
We stabilize your data architecture first. Then, we standardize metrics, clean pipelines, and enforce governance across sources. BI performs best when it sits on top of a well-structured, trusted data layer.
Why Your Company Needs Generative AI for Business Intelligence
Investing in Gen AI is a strategic necessity, not just a tech upgrade. It’s an essential tool required for any organization to stay competitive and innovative. The technology transforms data analytics and business intelligence by automating complex tasks and revealing deeper insights through pattern recognition. It modifies approaches to decision-making and planning.
When enterprises integrate generative AI into BI systems, they can process and analyze data faster and on a larger scale. This leads to well-informed, accurate, and timely judgments. AI’s speed and efficiency help companies quickly adapt to market changes, seize new opportunities, and build a strong brand reputation.
At Master of Code Global, we specialize in directing the power of Generative AI services to drive business growth and revenue. Our expertise lies in integrating artificial intelligence into your existing frameworks. We ensure that your business has access to the full spectrum of its capabilities. Our masters provide tailored solutions that align with your unique business needs and objectives.
How to Implement Generative AI for Business Intelligence: A Practical 3-Step Path
Step 1: Assess Business Objectives Before Choosing Technology
Our Master of Code Global team starts the process with decisions, not data. We examine where BI currently slows the organization down or fails to support timely action. Common signals include delayed reporting, low dashboard adoption, or heavy dependence on analysts for simple questions.
We define 2–3 concrete objectives AI should support, such as faster root-cause analysis, broader BI adoption among non-technical users, or earlier detection of risks and opportunities. Clear goals prevent overengineering and keep implementation focused on outcomes that matter.
Step 2: Prepare Your Data for AI-Driven Analysis
Clients are not expected to “fix their data” before engaging us. Our Master of Code Global experts handle data readiness as part of the implementation. Generative AI applied to BI is only as reliable as the data beneath it, so we review how data flows through the BI stack and identify where trust breaks down, from inconsistent definitions to fragmented sources and fragile pipelines.
We standardize key metrics, clean critical datasets, and set up clear access controls aligned with governance and security requirements. Preparation doesn’t mean perfection, but it does require a stable, well-governed data layer, and we take responsibility for getting it there.
Step 3: Select the Right Tool for Your BI Maturity
Tool selection and implementation are fully handled by the Master of Code Global team. You don’t need to evaluate platforms, compare vendors, or experiment with AI capabilities on your own. Not every BI environment needs the same level of AI sophistication, and we design the solution based on actual BI maturity.
We select, integrate, and configure the AI layer to fit existing BI workflows, governance rules, and enterprise data foundations. By prioritizing explainability, control, and seamless integration over novelty, we ensure AI-driven BI is adopted quickly and trusted across the organization.
The Future of Business Intelligence with Generative AI
Traditional BI was designed for a world where data was limited, structured, and reviewed after the fact. That world no longer exists, and the gap is widening.
When you integrate AI in your BI, it pushes the system into a new operating mode. Instead of describing what already happened, future systems explain what is happening now and suggest what to do next. Real-time insight, predictive signals, and prescriptive guidance become standard expectations, not advanced features.
According to a recent study, the most visible shift in AI trends in Business Intelligence will be from dashboards to dialogue. As natural language interfaces mature, interacting with BI will feel less like operating software and more like reasoning with a knowledgeable analyst. This lowers friction and brings analytics directly into decision moments, where timing matters most.
Another defining change in Generative AI trends is automation at scale. Data preparation, analysis, and reporting will increasingly run in the background. Human effort moves upstream, toward framing better questions, validating assumptions, and acting on insights.
Generative AI also reshapes who BI is for. As technical barriers fall, analytics spreads beyond specialist teams. Managers, operators, and executives access insights independently, reducing bottlenecks while increasing organizational alignment around data.
At the same time, the future of BI will demand stronger foundations. Explainability, governance, and data quality will determine whether AI-driven insights are trusted or ignored. Organizations that invest early in architecture and transparency will move faster than those that don’t.
The direction is clear. Business intelligence is no longer a reporting layer at the end of a workflow.
With Generative AI, you’re not just keeping up; you’re setting the pace in your industry. Connect with us at Master of Code Global. Together, let’s turn your data into a powerhouse of strategic opportunities.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to see how Generative AI can boost your company’s efficiency.






